
| 
|
You are hereGame theoryGame theory is a field of math that concerns optimal independent decision making by several players, when each decision affects the other players. It used to be very useful in many fields of science, eg in biology, economy, IT or social science. A good example of game theory's existence in everyday life can be the situation, where a driver is getting close to the zebra crossing and notices a pedestrian. The possibilities for a driver are to keep constant speed, speed up, slow down or stop. Pedestrian can wait for a car to pass through or not. Participants make their decisions keeping in mind what are the other's possible strategies and choosing the best option. Other example can be a producer deciding about the quality of product regarding to the market reaction and expected profit (the cost of production vs profit from the sale of product). Let's consider a number of players, and assume that each makes an independent decision. Each player can choose one of the set of its own strategies – available decisions. A complete set of players with a particular decision chosen by each one is a point in a multidimensional space that contains scores for each players in this actual situation. The higher the score rate, the more favorable is this situation for a player. A Hicks optimum is a point in a space in which the sum of scores for all players is the highest in the whole space. A Nash equilibrium is a point in a space in which no one would change his decision, if they knew decisions of the other players before. An attractor here is a Nash equilibrium and also an area where other points from the space would evolve towards that equilibrium (according to preference directions of players). A set of points aiming at one attractor defines its basin of attraction. An example game theory's problemOne of common examples of applying game theory is a Prisoner's Dilemma. The intuition is here as following. Two people were caught on failed attempt of robbery. They are also suspects of a serious crime. Though, there are no proofs against them. After being separated, they both get a possibility of testifying against the other in exchange for commuting a sentence. In this problem they both have 2 strategies available (cooperation and keeping silence). After making decisions by both prisoners, they will get to know the effects (see the score matrix, Fig. 1). In case of keeping silence by both prisoners, no one will have a benefit from this situation. When both cooperate, each prisoner is incriminated, yet the punishment is slightly softened. If one prisoner cooperates and second does not, the first one's punishment is softened and the second one becomes incriminated.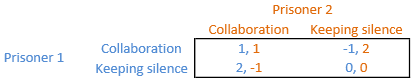 Fig. 1. An example score matrix Fig. 1. An example score matrix
The appletChoose the interface language: The applet – descriptionChoosing configurationThe application's main menu (Fig. 2) lets the user choose a configuration in 3 different ways:
Viewing the spaceWhen viewing the space, there are 2 modes available: edit mode and features mode. The shared components are:
The edit modeThe distinctive feature of the edit mode (Fig. 6) is a panel where the user can choose an element and change its scores for all the players. The x, y and z axes represent players, and the color in the panel corresponds to the proper axis in the space viewer. Changing the strategy for one of the players is equivalent to a transition in the space. The actual position (or the set defined by choices of some players) is emphasized with a distinct color in the space viewer. The features modeIn this mode (Fig. 7) there is a possibility to count the game theory features for a particular instance of a game. The mentioned features are Hicks optima and Nash equilibria with basins of attraction. The Hicks optima are emphasized with one distinct color. For Nash equilibria, each one found is shown with a unique color. The basins are visualized using the attraction factors and the colors of the appropriate attractors that correspond to a particular point in the space.
Technical details: the algorithms employedFinding the Hicks optima: for all the points in the space, the sum of scores for all players is being counted. The Hicks optimum is a point where the sum of scores is maximal. Finding the Nash equilibria and its attraction basins is described below.
Useful sources
|